
Pulmonary
Metastatic
Disease
Pulmonary
Metastatic
Disease
© Copyright William Herring, MD, FACR

SOLITARY METASTASES
MULTIPLE NODULES
Colon (30-40%)
Sarcomas, particularly from bone
Kidney
Testicle
Breast
Malignant melanoma
Kidney
· Thyroid
Sarcoma of bone
LYMPHANGITIC SPREAD
CAVITARY METS
Lesions arise around chest
Simulate CHF
Lung
Breast
Thyroid
Larynx
Stomach
Pancreas
Cervix
Usually thick walled with nodular innermargin
Squamous cell primaries such as
Head and neck tumors
Ca of the cervix
Transitional cell ca
Melanoma
Adenocarcinoma
Metastases to Lung

Types of Spread
Direct extension
Hematogenous
Lymphangitic

Direct ExtensionGeneral
Rare
Pleura is resistant to spread
Extension to ribs or vertebral body
Pancoast tumor
Extension to esophagus

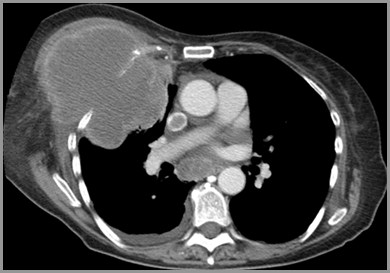
Direct Extension of Lung Cancer ThroughChest Wall

Hematogenous spreadGeneral
Produces showers of tumor emboli atdifferent times
Lung nodules–Cannonball lesions
Usually multiple and of varying sizes

Hematogenous spread By Cell Type
Adenocarcinoma
Colorectal
Breast
Renal
Most GU tumors
Squamous cell ca
Head and neck tumors in a male
Cervical ca in a female

Hematogenous Mets to LungCauses
Colorectal ca
Breast ca
Renal cell ca
Most GU tumors
Endometrial
Testicular
Malignant Melanoma
Soft tissue sarcomas

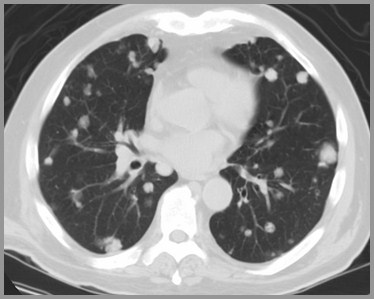
Hematogenous Metastases from ColonCancer

Lymphangitic SpreadGeneral
Probably hematogenous to lymphaticsthen retrograde to hila
Due to lymphatic blockade at hilus
Produces pulmonary interstitial edema
Does not clear as rapidly or completely asCHF
Pleural fluid may be benign at first

Lymphangitic SpreadAppearance
Laminar effusion
Kerley B lines
Fluid in the fissures
Peribronchial cuffing

Lymphangitic SpreadCauses
Lung ca
Breast ca
Gastric ca
Pancreatic ca
Thyroid ca
Laryngeal ca
Cervical ca

Lymphangitic Spread of Lung Cancer toRight Lung
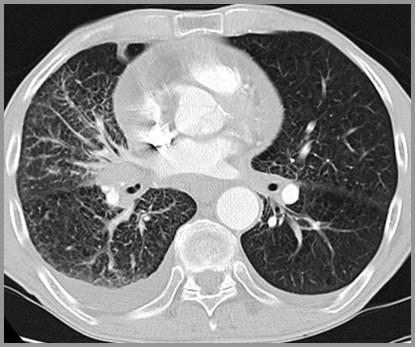

Patterns of Spread
Ovarian tumors usually spread locallyin peritoneum
Prostate ca rarely spreads to lung,usually retroperitoneum and bone
Cervical ca extends locally andproduces hydronephrosis
Renal cell ca often spreads to lung

Head and neck tumors spread locally
Sarcomas produce some of thefastest growing mets
Choriocarcinoma may haveindistinct margins
Patterns of Spread

Causes of Lung NodulesIn order
Granulomas
Bronchogenic carcinoma
Hamartomas
Metastases

Cavitating Nodules
Squamous cell ca—most common
Adenocarcinoma
Bronchoalveolar cell ca (rare)
Hodgkin's Disease (rare)

Cavitary Head and Neck Squamous CellCarcinoma
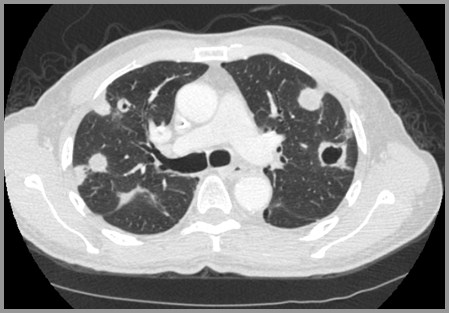

Pulmonary Nodules with Pneumothorax
Osteosarcoma
Wilm's tumor
Eosinophilic granuloma

The End